The Supreme Court ruled that it cannot order the inclusion of Rajasthani as an official language in the Constitution’s Eighth Schedule.
Approximately the eighth schedule
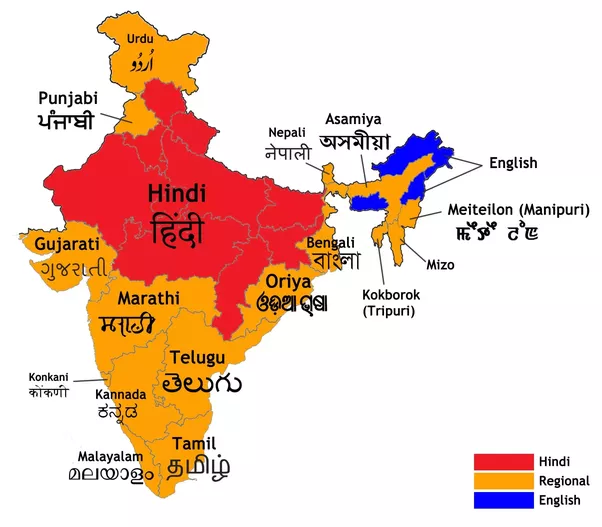
- The Republic of India’s official languages are listed in the Eighth Schedule.
- The Constitution has constitutional provisions relating to the Eighth Schedule in Articles 344(1) and 351.
- It was originally established to provide representation on the Official Languages Commission and to develop Hindi and English, the Union’s official languages.
- Candidates taking public service examinations have the option of answering exam papers in any language from the Eighth Schedule.
Languages included
- Assamese, Bengali, Bodo, Dogri, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Maithili, Malayalam, Manipuri, Marathi, Nepali, Odia, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Santali, Sindhi, Tamil, Telugu, and Urdu were among the 22 languages.
- Tamil (designated in 2004), Sanskrit (2005), Kannada (2008), Telugu (2008), Malayalam (2013), and Odia (2014) are among the classical languages.
Chronological Updates
- The Constitution’s Eighth Schedule previously featured 14 languages.
- Sindhi was included as part of the 21st Constitutional Amendment Act in 1967.
- The 71st Constitutional Amendment Act of 1992 included Konkani, Manipuri (Meitei), and Nepali.
- Bodo, Dogri, Maithili, and Santali were added as part of the 92nd Constitutional Amendment Act in 2003.
- The spelling “Oriya” was substituted with “Odia” by the 96th Constitutional Amendment Act in 2011.
Source: https://www.mha.gov.in/sites/default/files/EighthSchedule_19052017.pdf
